Dear visitor, welcome to
GNSS-
ULG
. To use full services of our website, please register.
Description
RTK ionospheric error
The RTK product quantifies the positioning error due to the ionosphere for RTK applications over Belgium. The stack plot represents the percentage of baselines affected by the ionospheric effect on an hourly basis, with a color code ranging from green (nominal conditions expected) to red (RTK positions extremely affected by the ionosphere). In addition, an RTK activity map giving “ionospheric conditions” for each baseline is produced every 15 min.
Read more about RTKIrregularities Calendar
Activity on -
Total Electron Content
Irregularities
Dst index
Ionospheric error on baseline length
Ionospheric error on baseline length
Sodipe MAP
Read more about RTK
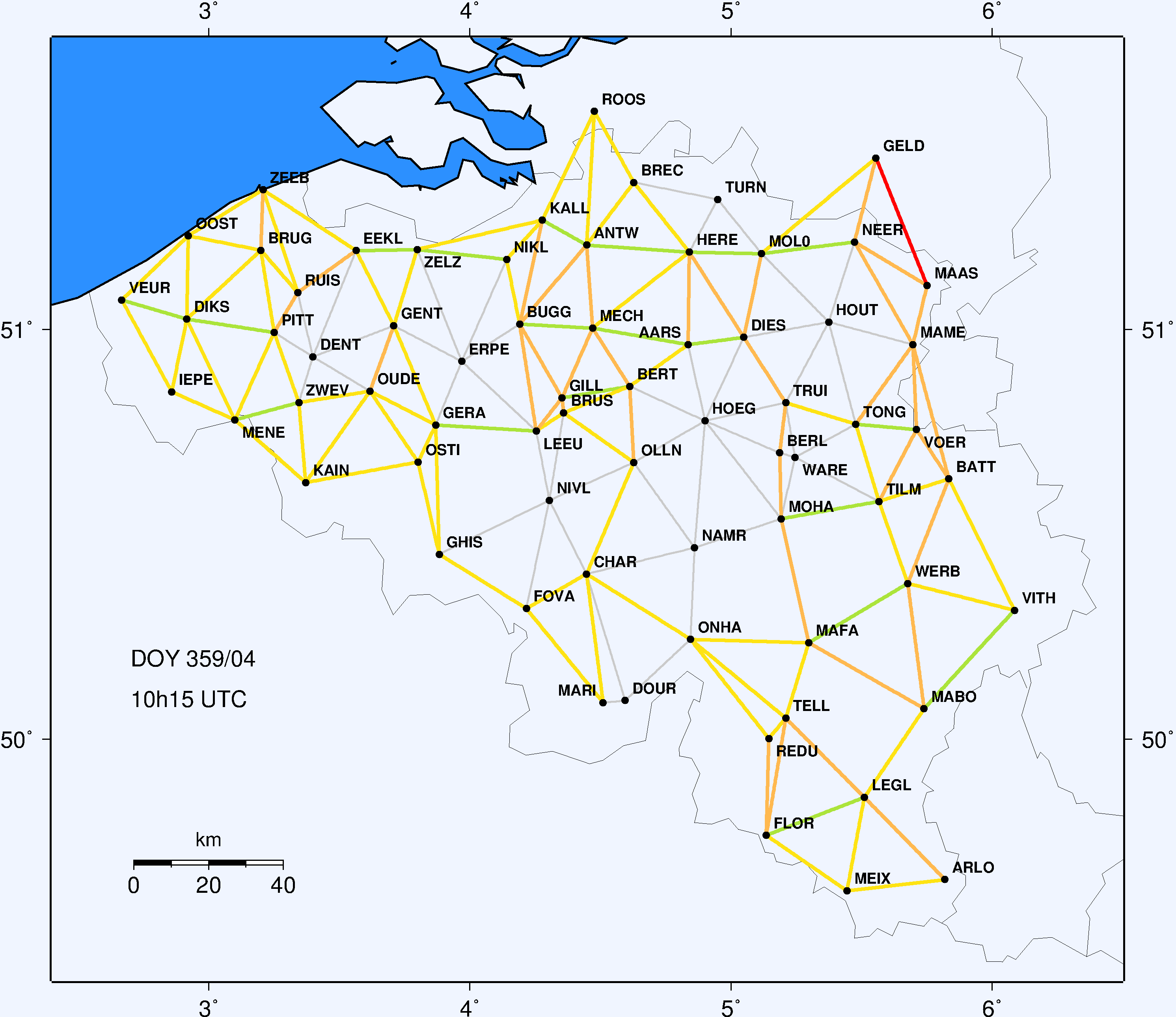
Precise positioning techniques in relative and differential modes, such as the Real-Time Kinematics (RTK), are affected by the ionospheric error. More precisely, gradients and irregularities in the Total Electron Content (TEC) are responsible for degrading positioning conditions.
The SoDIPE (Software for Determining the Ionospheric Positioning Error) software (Lejeune et al., 2012), provides the ionospheric positioning error for each baseline of the Belgian dense network of CORS (Continuously Operating Reference Stations) stations.
The product, presented in the form of stack plots summarizing the whole network, is available every hour.
Moreover, SoDIPE also produces a colored map every 15 min, as well as the time series of the ionospheric positioning error for each baseline (available when clicking on the baseline). The following color scale translates the different threat categories due to the ionospheric variability:
- Green conditions correspond to nominal conditions of the RTK, i.e. an ionospheric error smaller than 1cm + 1ppm.
- Yellow conditions are encountered if the error is within the interval [1cm + 1ppm ; 1cm + 3ppm].
- Orange conditions are encountered if the error is within the interval [1cm + 3ppm ; 1cm + 7ppm].
- Red conditions are related to error larger than 1cm + 7ppm.
Please note that the values related to the color scale have to be multiplied by the PDOP at the receiving station to give users a realistic estimation of the positioning error due to the ionosphere.
Lejeune S., Wautelet G., Warnant R. (2012), Ionospheric effects on relative positioning within GPS dense network, GPS Solutions, 16 (1), pp. 105-116, doi:10.1007/s10291-011-0212-1.
http://hdl.handle.net/2268/86750
The SoDIPE (Software for Determining the Ionospheric Positioning Error) software (Lejeune et al., 2012), provides the ionospheric positioning error for each baseline of the Belgian dense network of CORS (Continuously Operating Reference Stations) stations.
The product, presented in the form of stack plots summarizing the whole network, is available every hour.
Moreover, SoDIPE also produces a colored map every 15 min, as well as the time series of the ionospheric positioning error for each baseline (available when clicking on the baseline). The following color scale translates the different threat categories due to the ionospheric variability:
- Green conditions correspond to nominal conditions of the RTK, i.e. an ionospheric error smaller than 1cm + 1ppm.
- Yellow conditions are encountered if the error is within the interval [1cm + 1ppm ; 1cm + 3ppm].
- Orange conditions are encountered if the error is within the interval [1cm + 3ppm ; 1cm + 7ppm].
- Red conditions are related to error larger than 1cm + 7ppm.
Please note that the values related to the color scale have to be multiplied by the PDOP at the receiving station to give users a realistic estimation of the positioning error due to the ionosphere.
Lejeune S., Wautelet G., Warnant R. (2012), Ionospheric effects on relative positioning within GPS dense network, GPS Solutions, 16 (1), pp. 105-116, doi:10.1007/s10291-011-0212-1.
http://hdl.handle.net/2268/86750